Prognostic Significance of Preoperative C - Reactive Protein Elevation and Thrombocytosis in Patients with Non-Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Aim: The aim of this study was to investigate the association of preoperative C-reactive protein (CRP) elevation and thrombocytosis with the prognosis of patients with non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Materials and Methods: This was a retrospective review of the medical records of 43 patients (31 men and 12 women) with non-metastatic RCC who underwent a radical nephrectomy between August 2012 and August 2015 and for whom preoperative CRP and platelet data were available for analysis. Preoperative CRP elevation and thrombocytosis were compared with clinical and pathological variables.
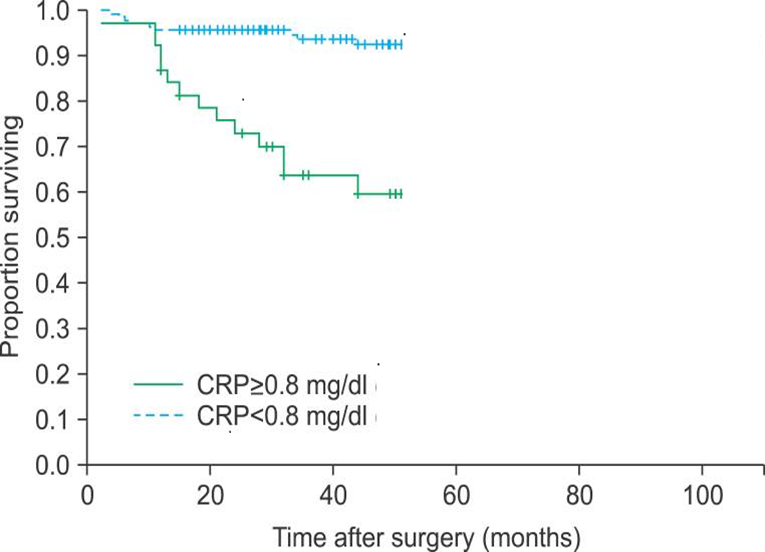
Results: There were 10 patients with CRP elevation and 6 patients with thrombocytosis. The mean follow-up time was 28.3 months (range- 13-47 months). Six patients (13.9%) developed metastases and one patient died during the follow-up period. CRP elevation was significantly correlated with anemia (p=0.001), T stage (p=0.004), grade (p=0.025), and metastasis (p<0.001). Thrombocytosis was significantly correlated with anemia (p=0.003), T stage (p=0.002), and metastasis (p=0.001). The univariate analysis identified anemia, CRP elevation, thrombocytosis, tumor histology subtype, tumor size, T stage, and grade as significant prognostic factors associated with recurrence-free survival, whereas the multivariate analyses showed that CRP elevation (p=0.033) and tumor size (p=0.007) were independent prognostic factors.
Conclusions: Preoperative CRP elevation and thrombocytosis were associated with a poorer prognosis and a higher recurrence rate in patients with non-metastatic RCC. Moreover, preoperative CRP elevation appeared to be an independent predictor of tumor recurrence and prognosis.
Preoperative thrombocytosis, however, was not an independent prognostic factor for tumor recurrence and prognosis.
Keywords: C-reactive protein, Prognosis, Renal cell carcinoma, Thrombocytosis
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Jemal A, Tiwari RC, Murray T, Ghafoor A, Samuels A, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2004. CA Cancer J Clin. 2004;54:8–29.
Gudbjartsson T, Thoroddsen A, Petursdottir V, Hardarson S, Magnusson J, Einarsson GV. Effect of incidental detection for survival of patients with renal cell carcinoma: results of population-based study of 701 patients. Urology. 2005;66: 1186–1191.
Balkwill F, Mantovani A. Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet. 2001;357:539–545.
Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, Fritz A, Balch CM, Haller DG, et al. American joint committee on cancer staging manual. 6th ed. New York: Springer-Verlag; 2002. pp. 323–328.
Fuhrman SA, Lasky LC, Limas C. Prognostic significance of morphologic parameters in renal cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1982;6:655–663.
Ballou SP, Kushner I. C-reactive protein and the acute phase response. Adv Intern Med. 1992;37:313–336.
Miki S, Iwano M, Miki Y, Yamamoto M, Tang B, Yokokawa K, et al. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) functions as an in vitro autocrine growth factor in renal cell carcinomas. FEBS Lett. 1989;250:607–610.
Guillem P, Triboulet JP. Elevated serum levels of C-reactive protein are indicative of a poor prognosis in patients with esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus. 2005;18:146–150.
Ito K, Asano T, Yoshii H, Satoh A, Sumitomo M, Hayakawa M. Impact of thrombocytosis and C-reactive protein elevation on the prognosis for patients with renal cell carcinoma. Int J Urol. 2006;13:1365–1370.
Karakiewicz PI, Trinh QD, Lam JS, Tostain J, Pantuck AJ, Belldegrun AS, et al. Platelet count and preoperative haemoglobin do not significantly increase the performance of established predictors of renal cell carcinoma-specific mortality. Eur Urol. 2007;52:1428–1436.
Komai Y, Saito K, Sakai K, Morimoto S. Increased preoperative serum C-reactive protein level predicts a poor prognosis in patients with localized renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 2007;99:77–80.
Casamassima A, Picciariello M, Quaranta M, Berardino R, Ranieri C, Paradiso A, et al. C-reactive protein: a biomarker of survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with subcutaneous interleukin-2 based immunotherapy. J Urol. 2005;173:52–55.
Pedersen LM, Milman N. Prognostic significance of thrombocytosis in patients with primary lung cancer. EurRespir J. 1996;9:1826–1830.
Göðüþ C, Baltaci S, Filiz E, Elhan A, Bedük Y. Significance of thrombocytosis for determining prognosis in patients with localized renal cell carcinoma. Urology. 2004;63:447–450.
Bensalah K1, Leray E, Fergelot P, Rioux-Leclercq N, Tostain J, Guillé F, PatardJJ.Prognostic value of thrombocytosis in renal cell carcinoma.. J Urol. 2006 Mar;175(3 Pt 1):859-63.
K Inoue et al .Prognostic Significance of Thrombocytosis in Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients.Int J Urol 11 (6), 364-367. 6 2004
VivekVenkatramani, Arabind Panda, and Nitin S. Kekre. Is thrombocytosis a useful prognostic marker in renal cell carcinoma? Results of a single-center retrospective analysis.Indian J Urol. 2015 Jan-Mar; 31(1): 42–46.doi: 10.4103/0970-1591.145292.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An Initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr MGR Medical University
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities