Phenytoin Hypersensitivy Syndrome
Abstract
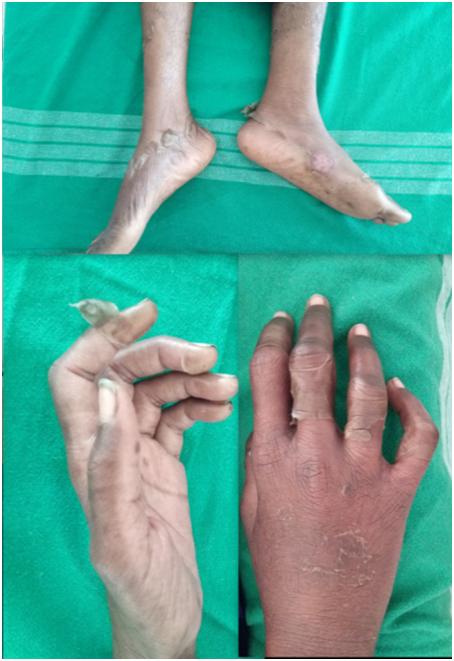
Anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome (ACHS) has been reported to occur with use of phenytoin, carbamazepine, phenobarbitone and lamotrigine, but not valproate. It is a rare and potentially fatal complication. ACHS is indicated by the presence of a triad of characteristic clinical features — fever, rash and internal organ involvement. It is estimated to occur in about 1 in 1000 to 1 in 10,000 patients who are exposed to these anticonvulsants. Case scenario : A 27 year old female was taken to government hospital with complaints of diffuse edema over face, hands and legs, acute eczematous changes with oozing and crusting around the eyes, nose, neck, upper-limb and abdomen. Bilateral pitting edema was present. Erythematous macules present over both legs. Oral and genital mucosa is normal. The patient was abruptly stopped with all the medications and managed with corticosteroids and shifted over to Tablet. Clobazam 10mg. Discussion : We present a case report of a patient with characteristic features of the phenytoin hypersensitivity syndrome (PHS), after treatment with phenytoin. In addition to the clinical picture, and the absence of a septic focus, the probable response to corticosteroid therapy is compatible with the diagnosis of PHS. Conclusion : The patient described in this report, presented to hospital with severe skin lesions and features following the use of phenytoin. Such a rapidly fulminating form of PHS has not been well documented. The early recognition of this syndrome and the institution of corticosteroids may have been responsible for the favorable outcome in this case
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Lippincott’s illustrated reviews: Pharmacology (7thed.). Wolters Kluwer (India) Pvt Ltd 2015. P.160
Tripathi KD. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology (7thed). Jaypee brothers Medical publishers (P) Ltd; 2014. P.413-415
Silber IB, Epstein JW. The treatment of chorea with phenylethylhydantoin: a study of 28 cases. Arch Pediatr 1934;51:373-82
Goodman & Gilman’sThe Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics(12thed). Mcgraw hill 2011. P.590-593
Knowles SR, Shapiro LE, Shear NH. Anticonvulsant Hypersensitivity Syndrome. Drug Safety, December 2, 1999; Vol 6: 489-501
Schlienger R, Knowles S, Shear N. Lamotrigine associated anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome. Neurology, 1998; Vol 51: 1172-1175.
Bertram G, Susan B, Anthony J. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology (13thed). Mcgraw hill 2012.
Shear NH, Spielberg SP. Anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome. J Clin. Invest, December 1988; Vol 82: 1826-1832
Roujeau J, Stern R. Severe adverse cutaneous reactions to drugs. The New England Journal of Medicine, November 10, 1994; Vol 331, No. 19: 1272-1285.
Kaur S, Sarkar R, Thami GP, Kanwar AJ. Anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome. Pediatric Dermatology, 2002; Vol 19, No.2: 142-145
Mahadeva U, Al-Mrayat M, Steer K, et al. Fatal phenytoin hypersensitivity syndrome. Postgrad Med J1999; 75: 734-736
Potter T, DiGregorio F, Stiff M, Hashimoto K. Dilantin hypersensitivity syndrome imitating Staphylococcal toxic shock. Arch Dermatol1994;130:856–8.
Kleier RS, Breneman DL, Boiko S.Generalized postulation as a manifestation of the anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome. Arch Dermatol1991;127:1361–4.
Bessmertny O, Hatton RC, Gonzalez-Peralta RP. Antiepileptic hypersensitivity syndrome in children. The Annals of Pharmacotherapy. May 2001; 35: 533-538
Descamps V, Bouscarat F, Laglenne S, et a1. Human herpesvirus 6 infection associated with anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome and reactive haemophagocytic syndrome. Br J Dermatol 1997;137: 605-8.
Krauss G. Current understanding of delayed anticonvulsant hypersensitivity reactions. Epilepsy Currents2006; 6: 33-37
Gogtay NJ, Bavdekar SB, Kshirsager NA. Anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome: a review. Expert Opin Drug Saf2005; 4: 571-581
Handfield-Jones SE, Jenkins RE, Whittaker SJ, Besse CP, McGibbon DH. The anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome. Br J Dermatol1993;129:175–7.
Carmela C, VittorioMD, Jennie J, Muglia MD. Anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome. Arch Intern Med1995;155: 2285–90.
Flowers FP, Araujo OE, Hamm KA. Phenytoin hypersensitivity syndrome. J Emerg Med1987; 139: 367-368.
Parker WA. Shearer CA. Phenytoin hepatotoxicity; A case report and review. Neurology 1979; 29:175-178
De Vriese ASP, Philippe J, Van Renterghem DM, De Cuyper CA, et al. Carbamazepine Hypersensitivity Syndrome: report of 4 cases and review of the literature. Medicine1995;74:144¬52.
Choudary S, Mcleod M, Torchia D, Romanelli P. Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) Syndrome.J Clin AesthetDermatol. 2013;6(6): 31–37.
Kumari R, Timshina DK, Thappa DM. Drug hypersensitivity syndrome. Indian J DermatolVenereolLeprol2011;77:7-15
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr M.G.R. Medical University