A Case of Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia
Abstract
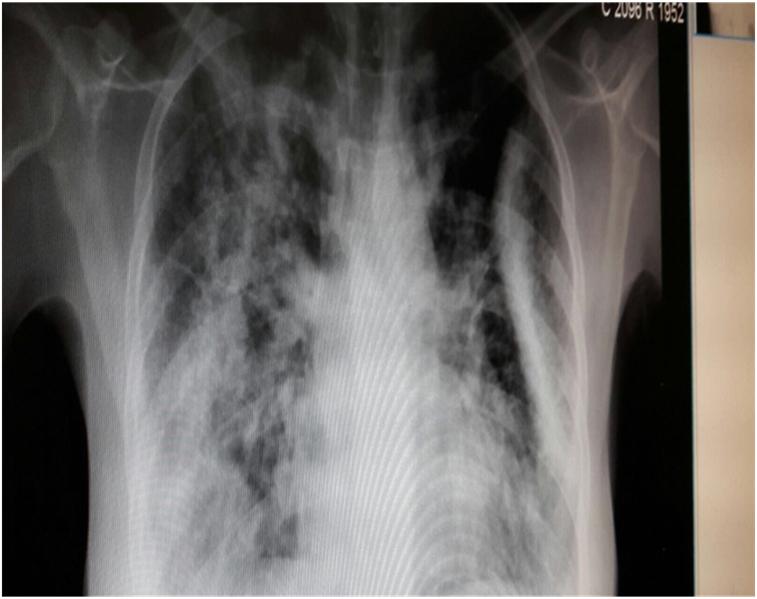
22 year old female ,a college student referred from nearby government medical College hospital as a case of ? H1N1 viral pneumonia. Patient presented with H/O non productive cough for 3 months and progressive dyspnea for 2 weeks, fever with night sweats for 2 weeks and with loss of appetite and loss of weight. She was treated at nearby hospital as a case of H1N1 pneumonia because of the clinical picture at the time of admission and due to the epidemic of H1N1 influenza during that period. Since She was still symptomatic despite antibiotics and antivirals, she was referred here for further management. At the time of admission, Patient was febrile, dyspneic and tachypneic, bilateral crepitations and wheeze present. Investigations revealed peripheral blood eosinophilia and x ray chest shows bilateral middle lobe and lower lobe infiltrates. CT chest showing the features of ‘Reverse Bat wing’s sign’ raised the suspicion and the dramatic clinical, radiological and serological improvement with oral corticosteroids clinched the diagnosis of Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia i.e., Pulmonary infiltrates with eosinophilia.
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Chitkara RK, Krishna G. Parasitic pulmonary eosinophilia. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2006; 27:171-84.
Carrington CB, Addington WW, Goff AM, et al: Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia.NEngl JMed 280:787–798, 1969.
Chang HW, Leong KH, Koh DR, et al: Clonality of isolated eosinophils in the hypereosinophilic syndrome. Blood 93:1651–1657, 1999.
Chusid MJ, Dale DC, West BC, et al: The hypereosinophilic syndrome: Analysis of fourteen cases with review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 54:1–27, 1975.
Cottin V, Cordier JF: Eosinophilic pneumonias. Allergy 60:841–857, 2005.
Durieu J, Wallaert B, Tonnel AB: Long-term follow-up of pulmonary function in chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. Groupe d’Etude en Pathologie Interstitielle de la Societe de Pathologie Thoracique du Nord. Eur Respir J 10:286–291, 1997.
Garrett JK, Jameson SC, Thomson B, et al: Anti-interleukin- 5 (mepolizumab) therapy for hypereosinophilic syndromes. J Allergy Clin Immunol 113:115–119, 2004.
Gleich GJ, LeifermanKM,Pardanani A, et al: Treatment of hypereosinophilic syndrome with imatinib mesilate. Lancet 359:1577–1578, 2002.
Hardy RW, Anderson RE: The hypereosinophilic syndromes. Ann InternMed 68: 1220–1229, 1968.
Johkoh T, Muller NL, Akira M, et al: Eosinophilic lung diseases: Diagnostic accuracy of thin-section CT in 111 patients. Radiology 216:773–780, 2000.
Marchand E,Reynaud-GaubertM,LauqueD, et al: Idiopathic chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. A clinical and follow-up study of 62 cases. The Groupe d’Etudes et de Recherche sur lesMaladies “Orphelines” Pulmonaires (GERM“O”P). Medicine (Baltimore) 77:299–312, 1998.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr M.G.R. Medical University