BILATERAL PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA A CASE REPORT
Abstract
Pheochromocytoma is a tumor of the
catecholamine-producing cells of the adrenal
medulla. These tumors produce
excess catecholamine, which if missed
or not properly treated, will almost prove
fatal. Therefore prompt diagnosis and
treatment is necessary. We present a
case of bilateral pheochromocytoma in a
young male who presented with complaints
of sweating, headache, tachycardia
and hypertension. Biochemical
evaluation showed excess catecholamine
production. Imaging studies
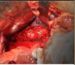
showed bilateral adrenal mass. Patient
underwent bilateral adrenalectomy after
thorough preoperative preparation. Histopathology
examination confirmed pheochromocytoma
bilaterally.
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Manger WM, Gifford RW (2002)
Pheochromocytoma. J Clin Hypertens
:62–72
Jennifer MJ Schreinemakers,
Bernard A Zonnenberg, Jo WM
Höppener,Frederik J Hes, Inne
HM Borel Rinkes and Cornelis JM
Lips
A patient with bilateral pheochromocytoma
as part of a VonHippel-Lindau
(VHL) syndrome type 2C World Journal
of Surgical Oncology 2007, 5:112
Godellas CV. Surgical approach to
adrenal neoplasms: laparoscopy versus
open adrenalectomy. Surg Oncol Clin N
Am 1998; 7: 807-817
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An Initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr MGR Medical University
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities