PRIMARY B CELL LYMPHOMA OF JEJUNUM - A RARE CASE REPORT
Abstract
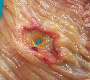
Abstract : Gastrointestinal lymphoma is a relatively rare tumor representing 0.9 percent of all primary GI malignant neoplasms. It is the most common form of extra nodal lymphoma.(1) Lymphoma presents with nonspecific abdominal pain in 70-80 percent of cases and weight loss in 30 percent. Lymphadenopathy, Pulmonary hilar adenopathy, and hepatosplenomegaly, all classic for disseminated lymphoma are usually absent in intestinal lymphoma. An abdominal mass may be palpable in 40-60 percent of patients. Other presentations may include perforation (up to 25 percent), obstruction, or intussusception.(2)Presenting an interesting and rare case of Primary B cell Lymphoma of Jejunum who presented with Intestinal Perforation.
Keyword :Primary B-cell Lymphoma, Intestinal Perforation
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Gulgun Engin, Ugur Korman, Gastrointestinal Lymphoma: a spectrum of fluoroscopic and CT findings, Diagnostic Interventional Radiology 2011; 17: 255-265
Muhammad Akram Dogar,Ayesha, Wasif majeed Chaudhary, King Edward Medical University, Mayo Hospital, Lahore. A rare case of Primary B cell Lymphoma of Jejunum: pjmhsonline.com
Gurney KA, Cartwright RA. Increasing incidence and descriptive epidemiology of extranodal non- Hodgkin lymphoma in parts of England and Wales. Hematol J 2002;3:95–104.
Ghai S, Pattison J, Ghai S, O’Malley ME, Khalili K, Stephens M. Primary gastrointestinal lymphoma: spectrum of imaging findings with pathologic correlation. Radiographics 2007; 27:1371–1388.
Dawson IM, Cornes JS, Morson BC. Primary malignant tumors of the intestinal tract. Br J Surg 1961;49:80–89.
Isaacson PG. Gastrointestinal lymphomas of Tand B-cell types. Mod Pathol 1999;12:151–158.
Green PH, Fleischauer AT, Bhagat G, Goyal R, Jabri B, Neugut AI. Risk of malignancy in patients with celiac disease. Am J Med 2003;115:191–195.
Card TR, West J, Holmes GK. Risk of malignancy in diagnosed celiac disease: a 24-year prospective, population-based, cohort study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2004;20:769–775.
Smedby KE, Akerman M, Hilderbrand H, Glimelius B, Ekbom A, Askling J. Malignant lymphomas in celiac disease: evidence of increased risks for lymphoma types other than enteropathy-type T cell lymphoma. Gut 2005;54:54–59.
Rohatiner A, d’Amore F, Coiffier B, et al. Report on a workshop convened to discuss the pathological and staging classifications of gastrointestinal tract lymphoma. Ann Oncol 1994;5:397–400.
Cho KC, Baker SR, Altemann DD, Fuscoo JM, Cho S. Transpyloric spread of gastric tumors: comparison of adenocarcinoma and lymphomas. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1996;167:467–469.
Rubesin SE, Furth EE. Other tumors of the colon. In: Gore RM, Levine MS, eds. Textbook of gastrointestinal radiology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders, 2000; 1049–1074.
Amer MH et al. Gastrointestinal lymphomas in Adults. Gastroenterology 1994; 106: 846-858.
Talamonti MS et al. Gastrointestinal Lymphoma. Arch Surg 1990: 125: 972-977.
List AF et al. Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma of the gastrointestinal tract: An analysis of clinical and pathologic features affecting outcome. J Clin Onc 1988; 6: 1125-1133
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An Initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr MGR Medical University
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities