Curettage and Bone Grafting for Monostotic fibrous dysplasia - A case report
Abstract
Abstract : INTRODUCTION Fibrous dysplasia is a common
benign tumour comprising of 5-7 percent of benign bone
tumours - most commonly affecting long bones. Bone pain is
the commonest mode of presentation of monoostotic fibrous
dysplasia. Herewith presenting a case of mono-ostotic fibrous
dysplasia treated with curettage and bone graft with a
combination of autograft and allograft. MATERIALS AND
METHODS A 17 year old male presented with left hip pain of
1 year duration which restricted activities of daily living.
Examination revealed normal range of movements. X rays
revealed the presence of bony cyst - fibrous dysplasia.
Skeletal survey ruled out other bone involvement. Mirels
criteria had a score of 10 suggesting the need for prophylactic
fixation to prevent pathological fracture. Through lateral
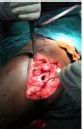
approach the cyst was approached. A cortical window was
created and cystic contents removed and sent for biopsy.
Complete curettage of the lesion done. The cavity was
packed with autograft harvested from ipsilateral iliac crest and
allograft from 2 femoral heads. RESULTS The biopsy report
confirmed the diagnosis of fibrous dysplasia. The patient had
uneventful post operative period. Upon 1 year follow up the
patient has returned to previous activity levels and
improvement in pain according to visual analogue scale.
Pathological fracture has also been prevented and the lesion
has not progressed in size.
CONCLUSION
Curettage and bone grafting is a simple and effective
procedure for the treatment of mono-ostotic fibrous dysplasia.
The amount of graft needed to fill the cavity after curettage
may be large and may need allograft in addition to
autogenous cancellous bone
Keyword :Monostotic fibrous dysplasia, impending
pathological fracture, auto-allograft
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Coley BL. Neoplasms of bone and related conditions; etiology,
pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. 2nd ed. New York:
Hoeber; 1960.
Campanacci M. Bone and soft tissue tumours: clinical features,
imaging, pathology and treatment. 2nd ed. New York: Springer;
Weinstein LS, Chen M, Liu J. Gs (alpha) mutations and imprinting
defects in human disease. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2002; 968:173-97.
Liens D, Delmas PD, Meunier PJ. Long-term effects of intravenous
pamidronate in fibrous dysplasia of bone. Lancet. 1994;
:953-4.
Stephenson RB, London MD, Hankin FM, Kaufer H. Fibrous
dysplasia. An analysis of options for treatment. J Bone Joint Surg
Am. 1987; 69:400-9.
Nakashima Y, Kotoura Y, Nagashima T, Yamamuro T,
Hamashima Y. Monostotic fibrous dysplasia in the femoral neck. A
clinicopathologic study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984;191:242-8.
Fibrous Dysplasia. Pathophysiology, Evaluation, and Treatment
J Bone Joint Surg Am. 87:1848- 1864, 2005 Matthew R. DiCaprio
and William F. Enneking
Lichtenstein L. Polystotic fibrous dysplasia. Arch Surg 1938 ; 36 :
-898 IMAGES
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An Initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr MGR Medical University
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities