A RARE PRESENTATION OF BILATERAL VESTIBULAR SCHWANNOMAS
Abstract
Abstract : OBJECTIVE We report a rare presentation of
bilateral vestibular schwannomas with left eye ptosis with
ophthalmoplegia.CASE REPORT An 18 year old female
patient was referred from Ophthalmology department to ENT
department with one year history of left eye lid drooping and
hard of hearing left ear. Pure tone audiogram showed left ear
moderate SN hearing loss and right ear mild SN hearing loss.
Brain Stem Evoked Response Audiogram showed wave III
and wave V latency on both sides more on left
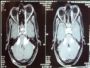
side.Gadolinium enhanced MRI brain showed bilateral
acoustic neuroma with neurofibromatous changes in the left
eye retro orbital area with medial rectus
hypertrophy.CONCLUSION Ptosis with ophthalmoplegia has
rarely been reported in NF2. In our case described, left eye
ptosis with ophthalmoplegia was caused by mechanical effect
of mass in retro orbital area.In this case since the tumors on
the both sides more than 1.5cm, the best option is regular
follow up eventhough she had moderate hearing loss on the
left side. Patient was advised for correction of left eye ptosis,
but she was not concerned about it and deferred surgery. So
she was advised regular follow up annually for clinical,
audiological and radiological evaluation.
Keyword :Bilateral Vestibular Schwannomas, Brain Stem
Evoked Response Audiogram, Gadolinium
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Martuza RL, Eldridge R: Neurofibromatosis2 (bilateral acoustic
neurofibromatosis) N Eng J Med 318: 684,1998.
Evans DG, Huson SM, Donnai D, et al; A genetic study of type 2
neurofibromatosis, in the united kingdom. Prevalence, mutation
rate, fitness and confirmation of maternal transmission effect on
severity. J Med Genet 29:841-846,1992.
Antinheimo J, Sankila R, Carpen O, et al: Population based
analysis of sporadic and type 2 neurofibromatosis-associated
meningiomas and schwannomas. Neurology 54: 71-76,2000.
Neurofibromatosis Conference Statement. National Institutes of
Health Consensus Development Conference. Arch Neurol 1988:
; 575-8.
Bouzar EA, Parry DM, Eldidge R, Kaiser-Kupfer MI: Visual
impairment in patients with neurofibromatosis2 .Neurology 43: 622-
,1993.
Neurofibromatosis 2- a case report. NA Pendse, V Menghani.
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging 2003; 13: 99-101.
Osborn Anne G,. Disorders of Histiogenesis: Neurocutaneous
Syndromes. Diagnostic neuroradiology: Mosby-Year Book 1994:
-93.
Evans DG and his collegues. Management of patient and family
with NF2. A Consensus Conference Statement. Br J Neurosur
; 19(1): 5-12.
Briggs R, Brackmann D, Baser M, Hitselberger W.
Comprehensive Management of bilateral acoustic neuromas. Arch
Oto Head Neck Surgery 120: 1307,`1994.
Farrell CJ and Plotkin SR. Genetic causes of brain tumors:
neurofibromatosis2, tuberosous sclerosis, Von Hippel-Lindau and
other syndromes. Neurol Clin 25: 925-946.
Otto SR et al. Multichannel auditory brainstem implant. Update
on performance in 61 patients. J. Neurosurgery 96:1063-1071.
Mathieu D et al (2007). Stereotactic radiosurgery for vestibular
schwannomas in patients with neurofibromatosis type 2. An
analysis of tumor control, complications and
having preservation rates. Neurosurgery 60;460-468.
Evan DG et al.(2006) Malignant transformation and new
primary tumors after therapeutic radiation for benign
disease. Substantial risks in certain tumors prone
syndromes. J Med Genet 43; 289-294.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An Initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr MGR Medical University
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities