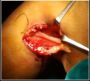
PERIPHERAL NERVE THICKENING NOT ALWAYS HANSENS A CASE REPORT
Abstract
Peripheral nerve thickening is
an important sign which is helpful in diagnosis
of few diseases. In Asian countries
especially where the prevalence of Hansens
disease is high, a high index of suspicion
is needed for diagnosis of other
causes of peripheral nerve thickening as
one could be mislead with the diagnosis
of Hansens disease and intervention at
the right time could prevent the neurological
sequelae of the disease causing
the peripheral nerve thickening. We report
a case of neurofibroma with gross
enlargement of common peroneal nerve
who was misdiagnosed to have Hansens
disease which lead to neurological sequelae.
Full Text:
PDFReferences
REFERENCES:
Michael Donaghy, Enlarged peripheral
nerves, Department of Clinical Neurology,
University of Oxford, Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford
OX2 6HE, UK Practical Neurology,
, 3, 40–45
Girdhar BK. Neuritic leprosy. Indian J
Lepr 1996; 68:35-42.
Jennekens FGI, van Brakel WH. Neuropathy
in leprosy In Latov N, Wokke JHJ,
Kelly JJ Jr (eds). Immunological and infectious
diseases of the peripheral
nerves.Cambridge: Cambridge Univ
Press, 1998; 319-39
Mahajan PM, Jogaikar DG, Mehta JM.
A study of pure neuritic leprosy: Clinical experience.
Indian J Lepr 1996; 68:137-41.
Rosser T, Packer RJ. Neurofibromas in
children with neurofibromatosis 1. J Child
Neurol 2002; 17:585–91.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An Initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr MGR Medical University
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities