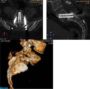
Transsacral Interbody Fusion for L5S1 High Grade Spondylolisthesis- Our Experience.
Abstract
In high-grade spondylolisthesis the distorted
anatomy due to forward slippage
of L5 over S1, a high degree of sacral
inclination, an unfavourable slip angle,
and loss of normal lordosis make conventional
approaches to 360 degree fusion
difficult or hazardous.Traditional
posterior instrumentation with posterolateral
fusion is associated with a high
rate of slip progression because the construct
fails to provide anterior column axial
load sharing and to restrict shear
forces across the disc space. Interbody
grafting is of marginal efficacy because
of the limited endplate surface area available
to create an interface with a
graft.Several innovative techniques have
been described to achieve successful
arthrodesis in this setting .We present
three cases of high grade , L5-S1
spondylolisthesis with sciatica and instability
pain who were managed with three
different techniques
,namely,transsacral intervertebral pedicle
screw fixation ,transsacral intervertebral
pedicle screw fixation and transvertebral
fibular strut grafting,transsacral intervertebral
pedicle screw fixation and transvertebral
autograft filled cage. All three patients
were operated by the same surgeon under
intraoperative fluoroscopic guidance.
Clinical and functional outcomes were
analyzed using standard scores
(ODI,SRS,VAS) preoperatively and during
the recent follow up(26 months).Fusion
was analyzed at the end of 14 months in all
three patients. As fusion was inconvincing
with conventional radiographs we analyzed
fusion with a multislice helical topographic
scan with multiplanar reconstruction with
cage subtraction.Pain relief was good except
with transvertebral fibular strut grafting.
The ODI and SRS scores were significantly
better with transvertebral cage fixation
.3D- CT films showed a fracture of the
fibular autograft ,whereas a solid anterior
L5-S1 bridging fusion mass and
intracage graft incorporation was evident with
transvertebral cage.Transsacral intervertebral
screw fixation with transvertbral cage provides
a biomechanically stable construct capable of
anterior column axial load sharing and resisting
shear forces across the lumbosacral junction,
given the anatomical constraints accompanying
high-grade spondylolisthesis. The titanium
cage will not be resorbed, as is the case with
fibular allograft,and the autograft within it will
enable an interbody fusion to occur.
Full Text:
PDFReferences
W.F.Beringer,D.O.,Jean Pierre
Mobasser,M.D,et al.Anterior transvertebral
interbody cage withposterior
transdiscal pedicle screw instrumentation
for high-grade spondylolist
h e s i s . N e u r o s u r g F o -
cus,Vol.20,March 2006.
Fairbank JCT & Pynsent, PB (2000)
The Oswestry Disability Index. Spine
Vol 25(22):2940-2953.
Ikka Helenius MD.PhD, Tommi
Lamberg MD,PhD,Kalevi OstermanMD
PhD.et al. Posterolateral anterior
or circumferential fusion in situ
for high grade dysplasticspondylolisthesis
in young children-evaluation
using SCOLIOSIS RESEARCH SOCIETY
questionnair e .Spi ne
:31:2:190-196.
Ville Remes,MD PhD, Tommi
Lamberg,MD PhD.,et al..Long-term
outcome afterposterolateral,anterior
and circumferential fusion for highgrade
spondylolisthesis in children
and adolescents.MRI findings after
average of 17 year followup.
Spine2006;31:21:2491-2499.
J.R.Johnson,E.O’G.Kirwan.The
long term results of fusion in situ for
severe spondylolisthesis. JBone Joint
Surg(Br) Vol.65-B(1)January 1983.
Burkus JK, Lonstein JE, Winter RB, et
al: Long-term evaluation of adolescents
treated operatively for spondylolisthesis.
A comparison of in situ arthrodesis only
with in situarthrodesis and reduction followed
by immobilization in a cast. J Bone
Joint Surg Am 74:693–704, 1992.
Smith JA, Deviren V, Berven S, et al:
Clinical outcome of transsacral interbody
fusion after partialreduction for high-grade
L5-S1 spondylolisthesis. Spine 26:2227–
, 2001
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An Initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr MGR Medical University
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities