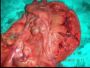
A CASE REPORT OF TORSION OF PSEUDOCYST OF WANDERING SPLEEN
Abstract
Wandering spleen is rare clinical entity
caused by absence or weakness of
splenic ligaments due to acquired or developmental
causes. It is usually seen in
pediatric age group, rarely seen in multiparous
females. Unusually long suspensory
ligaments of spleen leads to torsion
of splenic pedicle. It usually presents as
acute or chronic intermittent abdominal
pain. Pseudocyst formation is one of the
rare complication. Here we present a
case of Wandering spleen in a young female
presented with complication of
pseudocyst.
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Ben Ely A, Zissin R, Copel L, et al. The
wandering spleen: CT findings and possible
pitfalls in diagnosis. Clin Radiol2006;
: 954-8.
Buehner M, Baker MS. The wandering
spleen. Collective review. Surg Gynecol
Obst 1992; 175: 373-87.
Allen KB, Andrews G. Pediatric wandering
spleen - the case for splenopexy: review
of 35 reported cases in theliterature.
J Pediatr Surg 1989; 24: 432-35.
Shiels WE, Johnson JF, Stephenson SR,
et al. Chronic torsion of the wandering
spleen. Pediatr Radiol 1989;19:465–7
The Internal Journal of Radiology 2006:
Volume 5
Alimoglu O, Sahin M, Akdag M. Torsion
of a wandering spleen presenting with
acute abdomen: a case report. Acta Chir
Belg 2004; 10: 221-3.
Topilow AA, Steinhoft NG. Splenic pseudocysts,
a late complication of trauma. J
Trauma 1975;15:260–3.
Jones BJ, Daley M, Delaney PV. Torsion
of spleen managed by splenoplexy. Br J
Surg 1991;78:887–8.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An Initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr MGR Medical University
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities