Recurrent inspiratory stridor in a case of psoriasis due to post operative laryngospasm after Hemarrhoidectomy
Abstract
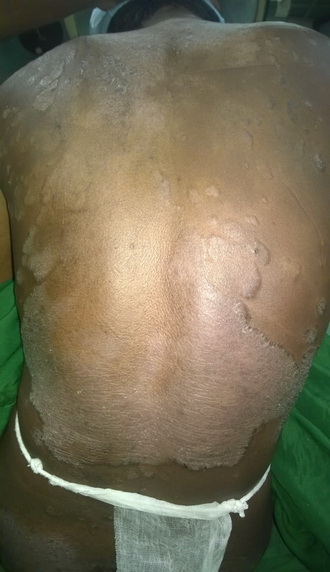
46 year old adult male , a case of chronic plaque psoriasis presented with grade III hemarrhoids and was posted for hemarrhoidectomy .Endotracheal general anaesthesia was preferred to central neuraxial blockade in this case and the course of surgery was uneventful .Patient was extubated at the end of the procedure. Laryngeal edema with recurrent laryngospasm was encountered in the post-operative period after tracheal extubation, which was successfully managed. Conduct of general anaesthesia for hemarrhoidectomy in this case has been elaborated . Laryngospasm - its cause , risk factors , modes of prevention , diagnosis and management have been reviewed . Anaesthetic implications in a case of psoriasis have been discussed .
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Pediatric laryngospasm - Journal compilation 2008 Blackwell Publishing Ltd, Pediatric
Anesthesia, 18, 303–307
Olsson GL, Hallen B. Laryngospasm during anesthesia. A computer-aided incidence study
in 136,929 patients. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1984; 28:567–575.
Ead H. Post-anesthesia tracheal extubation. Dynamics 2004; 15:20–25.
Doi M, Ikeda K. Airway irritation produced by volatile anaesthetics during brief inhalation:
Comparison of halothane, enflurane, isoflurane and sevoflurane.Can J Anaesth 1993;
:122–126.
Flick RP, Wilder RT, Pieper SF, et al. Risk factors for laryngospasm in children during
general anesthesia. Pediatr Anesth 2008; 18:289–296
Sumner E, Hatch D, (eds). Paediatric Anaesthesia, 2nd edn. London: Arnold, 1999.
Parnis SJ, Barker DS, Van Der Walt JH. Clinical predictors of anaesthetic complications
in children with respiratory tract infections. Paediatr Anaesth 2001; 11:29–40.
O’neill B, Templeton JJ, Caramico L, Schreiner MS. The laryngeal mask airway in
. pediatric patients: factors affecting ease of use during insertion an emergence. Anesth
Analg 1994; 78:659–662
Koc C, Kocaman F, Aygenc E et al. The use of preoperative lidocaine to prevent stridor
and laryngospasm after tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg
; 118: 880–882.
The Management and Treatment of Recurrent Postoperative Laryngospasm –ANESTH-
ANALG 1996; 83 : 1110 -1
Owen H. Post-extubation laryngospasm abolished by doxapram. Anaesthesia 1982; 37:
–1114.
.Sibai AN, Yamout I. Nitroglycerin relieves laryngospasm. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1999;
: 1081–1083.
Clinical review: Post-extubation laryngeal edema and extubation failure in
Critically ill adult patients. Critical Care 2009, 13:233 (doi: 10.1186/cc8142)
Psoriasis and Anesthetic considerations - M.E.J. ANESTH 20 (5), 2010
Marples RR, Heaton CL, Kligman AM: Staphylococcus aureus in psoriasis. Arch
Dermatol; 1973, 107:568.
Hattori S, et al: [Anesthetic management of a patient with erythroderma]. Masui - Jap J
Anes; 1996, 45(9):1127-30.
Trentham D, Le CH: Relapsing Polychondritis. Annals of Internal Medicine; 1998,
:114-122.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An Initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr MGR Medical University
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities