A Rare Case of Fibrous Dysplasia of Ethmoid Sinus – A Case Report & Review of Literature
Abstract
Introduction: Fibrous dysplasia is a benign skeletal lesion where the normal medullary bone is replaced by immature and fibrous stroma due to abnormal osteoblastic differentiation of unknown etiology.
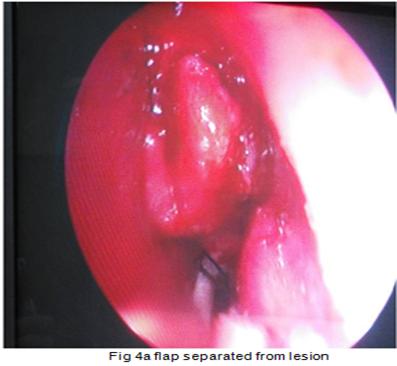
Case report : A 43 year old female with complains of nasal obstruction and anosmia found to have a bony hard mass between septum and middle turbinate. CT scan showed a fibroosseous lesion of ethmoid with ground glass appearance. Biopsy confirmed fibrous dysplasia. Endoscopic removal of mass was done.
Discussion:Fibrous dysplasia mostly occurs in the long bones, craniofacial bones are second common site of involvement. Fibrous dysplasia of paranasal sinus is rare. Conservative surgery is indicated for symptomatic patients.
Conclusion: Fibrous dysplasia is a rare disease of ethmoid sinuses. In limited lesion, an endoscopic sinus surgery could serve as an optimal treatment of choice.
Keywords: Fibrous dysplasia, Ethmoid
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Hyams VJ , Batsa kis JG, Michaelis L. Tumors of the upper respiratory tract and ear. Atlas of tumor pathology. Second series, Fascicle 25. Washington DC: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, 1 988.
Lichtenstein L. Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia. Arch Surg 1938; 36: 874–898.
Abdel-Wanis M, Tsuch iya H. Melatonin deficiency and fibrous dysplasia : lVI ight a relation exist? Medical Hypotheses. 2002 ; 59 : 552.
Tsai TL, Ho CY, Guo YC, et al. Fibrous dysplasia of the ethmoid sinus. J Chin Med Assoc 2003; 66: 131–133.
Dominok GW, Knoch HG. Knochengesch wuelste undgeschwulstaehnliche ochenerkrankungen, 3 rd edn. Jen a :V E B Gustav Fischer, 1982.
Engelbrecht V, Preis S, Hassler W, et al. CT and MRI of congenital sinonasal ossifying fibroma. Neuroradiology 1999; 41: 526–529.
Som PM, B ra ndwein IVI. Sinonasal cavities: Inflammatory diseases, tumors, fractures, a n d postoperative findings. I n :Som PM, Ca rton H D (eds). Head and neck imaging, 3rd ed n. St Lou is: Mosby-Year Book, 1 996: 233-43.
Jaffe H L Fibrous dysplasia of the bone. Bulletin of the New York Academy of Medicine. 1 946; 2 2 : 588-604
Diaz A, Danon M, Crawford J. McCune-Albright syndrome and disorders due to activating mutations of GNAS1. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2007;20(8): 853–880
FuYao-Shi, Perzin Karl H. (1974) : Non-epithelial tumors of the Nasal cavity, Paranasal sinuses and Nasopharynx : A Clinico-Pathologic study. II. Osseous and Fiobrosseous Lesions including Osteoma, Fibrous Dysplasia, Ossifying Fibroma, Osteoblastoma, Giant Cell Tumour and Osteosarcoma. Cancer 33; 1289-1305.
Lustig LR, Holliday MJ, McCarthy EF, et al. Fibrous dysplasia involving the skull base and temporal bone. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2001; 127: 1239–1247.
Commins DJ, Tolley NS, Milford CA. (1998) : Fibrous dysplasia and ossifying fibroma of the paranasal sinuses. J.Laryngology. Otology, 112(10) : 964-968.
Dornhoffer J, Schwager K. (1995) : Fibrous dysplasia and ossifying fibroma. 2 unusual fibro-osseous lesions of the paranasal sinuses. HNO, 43(3) : 193-196.
Von Rompaey D, Schmelzer B, Verstraete W, et al (1994) :Fibrous dysplasia in the fronto-ethmoidal complex :diagnosis and surgical aspects. Acta Otorhinolaryngology. Belgium 48(1): 37-40.
Pinsolle V, RiveI J, MicheletV, etal (1998) : Treatment of fibrous dysplasia of the cranio-facial bones. Report of 25 cases. Ann. Chir. Plast. Esthet. 43(3) : 234-239.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An Initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr MGR Medical University
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities