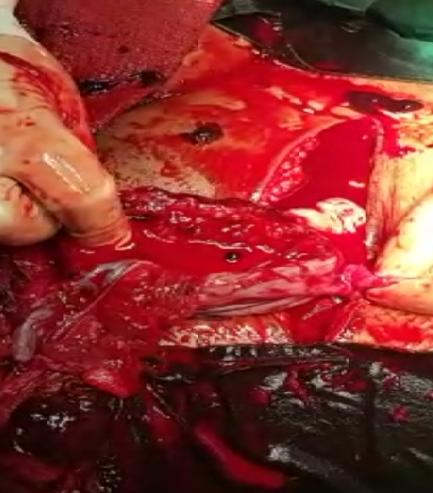
A Rare Case of Ruptured Rudimentary Horn Pregnancy
Abstract
Unicornuate uterus with non communicating rudimentary horn occurs due to incomplete fusion of mullerian ducts. Pregnancy in this horn is a rare phenomenon usually resulting in rupture during second trimester of pregnancy. Prerupture diagnosis of pregnancy in rudimentary horn with ultra sonography is technically difficult, with sensitivity of 30%. We report a case of ruptured non-communicating rudimentary horn at 20 weeks in a woman with previous Caesarean delivery. She presented to emergency in shock, with massive hemoperitoneum and ruptured horn. Intraoperatively a unicornuate uterus with rupture of non communicating rudimentary horn was confirmed and a dead fetus was found in peritoneal cavity with 2.5 liters of hemoperitoneum. Timely laparotomy, excision of the horn, and blood transfusion saved the patient. A high index of suspicion is warranted in cases of advanced gestation presenting with acute abdomen, especially in developing countries like India, where the possibility of early detection before rupture is unlikely, culminating in maternal demise.
Full Text:
PDFReferences
C. H. C. Hassan, A. Kadir, A. Karim, N. A. M. Ismail, and M. H. Omar, “Case report of ruptured non-communicating right rudimentary horn pregnancy: an acute emergency,” Acta Medica, vol. 54, no. 3, pp. 125–126, 2011.
C. Simon, L. Martinez, F. Pardo, M. Tortajada, and A. Pellicer, “Mullerian defects in women with normal reproductive outcome,” Fertility and Sterility, vol. 56, no. 6, pp. 1192–1193, 1991.
H. K. Sevtap, A. M. Aral, and B. Sertac, “An early diagnosis and successful local medical treatment of a rudimentary uterine horn pregnancy: a case report,” Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics, vol. 275, no. 4, pp. 297–298, 2007.
B. W. Rackow and A. Arici, “Reproductive performance of women with müllerian anomalies,” Current Opinion in Obstetrics and Gynecology, vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 229–237, 2007.
G. G. Nahum, “Rudimentary uterine horn pregnancy: the 20th-century worldwide experience of 588 cases,” Journal of Reproductive Medicine for the Obstetrician and Gynecologist, vol. 47, no. 2, pp. 151–163, 2002.
F. Mauriceau, Traite des maladaies des femmes grosses vol. 1, Compaigne des libraries, Paris, France, 1721.
J. L. O'leary and J. A. O'leary, “Rudimentary horn pregnancy,” Obstetrics and Gynecology, vol. 22, pp. 371–374, 1963.
L. Fedele, M. Dorta, P. Vercellini, D. Brioschi, and G. B. Candiani, “Ultrasound in the diagnosis of subclasses of unicornuate uterus,” Obstetrics and Gynecology, vol. 71, no. 2, pp. 274–277, 1988.
A. Tsafrir, N. Rojansky, H. Y. Sela, J. M. Gomori, and M. Nadjari, “Rudimentary horn pregnancy: first-trimester prerupture sonographic diagnosis and confirmation by magnetic resonance imaging,” Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine, vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 219–223, 2005.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An Initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr MGR Medical University
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities