Retrospective analysis of clinical profile, prognostic factors and outcomes of patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis
Abstract
Aim: To study the clinical profile, prognostic factors
and outcome in patients with emphysematous
pyelonephritis (EPN). Methods: All patients admitted with
a diagnosis of EPN between the period from March 2014
to March 2017 were included in this retrospective study.
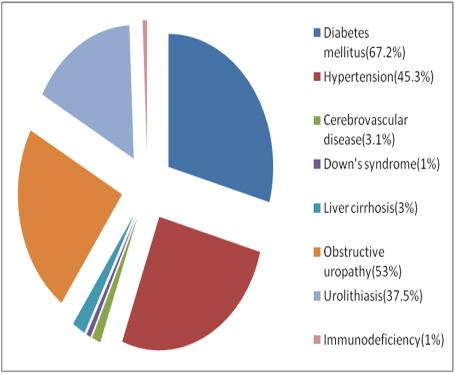
Results: Overall 64 cases were included in this study out
of which 49 were females, 15 were males. 43 (67.2%)
cases had type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. E.coli (64.1%) was the
commonest microorganism isolated in blood, urine and pus
culture. Presence of shock, DIC, increased serum
creatinine at the time of admission were identified as poor
prognostic factors. Severe hypoalbuminemia, need for
emergency dialysis and presence of polymicrobial infection
were significantly associated with failure of conservative
treatment. Conclusion: EPN requires special attention
because of its life threatening complications mainly due to
sepsis at the initial presentation, and outcome depends
upon the clinical course and prognostic factors.
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Ahlering TE, Boyd SD, Hamilton CL, Bragin SD,
Chandrasoma PT, Lieskovsky G, Skinner DG.
Emphysematous pyelonephritis: a 5-year experience with
patients. J Urol 1985, 134:1086–1088.
Ambar K, Ankur G, Devendara SR, Ashwini G, Anil B,
Dinesh K. Retrospective analysis of clinical profile and
prognostic factors of 19 patients of emphysematous
pyelonephritis. IntUrolNephrol 2009; 41: 959-966.
Basher AL, Manzoor AB, Mir IB, Mohd AG, Shahnaz AM,
Riyaz AD. Conservative management of emphysematous
pyelonephritis. Ind J EndocrinolMetab 2012; 16: 303-305.
Hildebrand TS, Nibbe L, Frei U, Schindler R. Bilateral
emphysematous pyelonephritis caused by Candida infection.
Am J Kidney Dis 1999; 33: 10-15.
Huang JJ, Tseng CC. Emphysematous pyelonephritis:
clinical radiological classification, management, prognosis
and pathogenesis. Arch Intern Med 2000; 60: 797-805.
James HLT, Chun KC, Ringo WHC, Inchak L, Chi-Kwan K,
Pak-Ling L, Fu-Keung C, Mong KY. Emphysematous
pyelonephritis: an 8 year retrospective review across four
acute hospitals. As J Surg 2013; 36: 121-125.
Kobayashi N, Yoshida K, Kamata S, Uchijima Y, Saitoh H.
A case of emphysematous pyelonephritis with disseminated
intravascular coagulation. Hinyokika Kiyo 1992; 38: 61-66.
Leons J, Humad SM, Sara YA. Emphysematous
pyelonephritis: Case report. Kuwait Med J 2004; 36: 134-136.
Matsuura H, Nakamura T, Inoue T, Yoshikawa K,
Hinoshita F. Case of emphysematous pyelonephritis with
sepsis and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Nihon
JinzoGakkai Shi 2008; 50: 140-146.
Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Kapur A. High
prevalence of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in
India: National Urban Diabetes Survey. Diabetologia 2001;
: 1094-1101.
Stapleton A. Urinary tract infections in patients with
diabetes. Am J Med 2002, 113:80–84.
Tseng CC, Wu JJ, Wang MC, Hor LI, Ko YH, HuangJJ.
Host and bacterial virulence factors predisposing to
emphysematous pyelonephritis. Am J Kidney Dis 2005;
: 432-439.
Soo Park B, Lee SJ, Wha Kim Y, Sik Huh J, Il Kim J,
Chang SG. Outcome of nephrectomy and kidney-preserving
procedures for the treatment of emphysematous
pyelonephritis. Scand J Urol Nephrol 2006, 40:332–338.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An Initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr MGR Medical University
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities