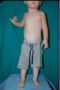
Waardenburg syndrome Type 2- A case report
Abstract
Abstract : Waardenburg syndrome (WS) is a rare
autosomally inherited disorder of neural crest cell
development characterized by varying degrees of hearing
loss and pigmentary changes affecting eye, hair and
skin.Four subtypes of the disease are recognized based on
the clinical presentation. A careful clinical evaluation is
required to differentiate various types of WS. We describe
here a case of WS Type 2 who presented to our outpatient
department.
Keyword :Waardenburg syndrome, sensorineural deafness,
heterochromia iridium
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Waardenburg PJ. A new syndrome combining
developmental anomalies of the eyelids, eyebrows and nose
root with pigmentary defects of the iris and head hair and
with congenital deafness. Am J Hum Genet 1951;3:195-253
Nayak CS, Isaacson G. Worldwide distribution of
Waardenburg Syndrome. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 2003;
: 817–820.
Read AP, Newton VE. Waardenburg syndrome. J Med
Genet 1997; 34: 656–665.
Farrer LA, Grundfast KM, Amos J, Arnos KS, Asher JH
Jr, Beighton P, Diehl SR et al. Waardenburg syndrome
(WS) type 1 is caused by defects at multiple loci, one of
which is near ALPP on chromosome 2: First report of the
WS Consortium. Am J Hum Genet 1992; 50: 902–913.
Delleman JW, Hageman MJ. Heterogeneity in
Waardenburg Syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 1977; 29: 468–
Bondurand N, Pingault V, Goerich DE, Lemort N, Sock E,
Le Caignec C, et al. Interaction among SOX10, PAX3 and
MITF, three genes altered in Waardenburg syndrome. Hum
Mol Genet 2000;9:1907-1
Liu XZ, Newton VE, Read AP. Waardenbur syndrome
type 2: phenotypic findings and diagnostic criteria. Am J
Med Genet 1995; 55: 95–100.
Tekin M, Bodurtha JN, Nance WE, Pandya A. Waardenburg
syndrome type 3 (Klein-Waardenburg syndrome)
segregating with a heterozygous deletion in the paired box
domain of PAX3: a simple variant or a true syndrome? Clin
Genet 2001;60:301-4
Gross A, Kunze J, Maier RF, Stoltenburg-Didinger G,
Grimmer I, Obladen M. Autosomal-recessive neural crest
syndrome with albinism, black lock, cell migration disorder
of the neurocytes of the gut, and deafness: ABCD
syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Apr 10;56(3):322-6.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr M.G.R. Medical University