FAUN TAIL NEVUS - A CUTANEOUS MARKER OF SPINAL DYSRAPHISM
Abstract
Abstract : Faun tail nevus is a posterior midline cutaneous
lesion that is a marker for its underlying spine and spinal cord
anomaly. Spinal dysraphism is a generic term describing
pathologic conditions related to improper closure of the
caudal neuropore. It encompasses all the conditions
associated with spina bifida. We report a series of four cases
with faun tail nevus who presented to our OPD over a period
of 2 years.All the four cases presented with complaints of
excessive hair growth in the lumbosacral region since birth.
one of the four patients had neurological manifestations like
difficulty in walking and weakness of the muscles of the lower
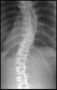
limbs with mild mental retardation. Radiological evaluation
revealed spinal abnormalities. Among the remaining three
patients who had no neurological manifestations, MRI of the
spine showed spinal dysraphism in two cases and one case
did not have any spinal abnormality.
Keyword :Faun tail nevus, spinal dysraphism
Full Text:
PDFReferences
velopmental
defects, 8 th ed, Vol. 3.Malden MA: Blackwell Publishing;
Rook’s textbook of dermatology-2010. p. 18.95-18.87.
Yamini M, Sridevi KS, Babu NP, Chetty NG. Faun tail nevus.
Indian Dermatol Online J [serialonline] 2011 [cited 2011 Dec 4];2:23
-4.
Wasnik AP, Shinagare A, Lalchandani UR, Gujrathi R, Pai BU.
Rudimentary third lower limb inassociation with spinal dysraphism:
Two cases. Indian J Orthop 2007;41:72-
Guggisberg D , Hadj-Rabia S , Vinay C et al. Skin markers of
o c c u l t d y s r a p h i s m i n c h i l d r e n : a
review of 54 cases. Arch Dermatol 2004; 1109-15
Drolet BA. Cutaneous signs of neural tube dysraphism. Pediatr
Clin North Am 2000;47:813-23.
Chopra S, Gulati MS, Paul SB, Hatirnota P, Jain R, Sawhney S.
M R I s p e c t r u m i n s p i n a l
dysraphism. Eur Radiol 2001; 11: 477- 505.
Tavafoghi V, Ghandchi A, Hambrick GW, Udverhelyi GB. Cutaneo
u s s i g n s o f s p i n a l d y s r a p h i s m .
Arch Dermatol 1978;114:573-7.
figures:[case1a][case1b][case1c][case1d][case2a][case2b][case2c]
[case2d][case3a][case3b][case3c][case4]
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr M.G.R. Medical University