An Unusual Cause For ExtraHepatic Portal Vein Obstruction– A Case Report
Abstract
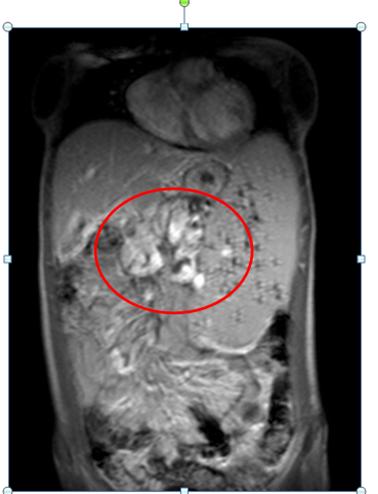
Extra Hepatic Portal Vein Obstruction is defined as“a vascular disorder of liver,characterized by obstruction of the extra-hepatic PV with or without involvement of intra-hepatic PV radicles orsplenic or superior mesenteric veins”. Etiological factors differ among pediatric and adult populations.Despite extensive history and laboratory work-up,many cases have been labelled idiopathic.However in our patient we were able to identify a unusual cause for EHPVO.
Keywords:ExtraHepatic Portal Vein Obstruction, Systemic lupus erythematosus
Introduction
Extrahepatic portal vein obstruction is a vascular disorder of the liver, which can results in obstruction and cavernous transformation of the portal vein with or without involvement of intrahepatic portal vein, splenic vein, or superior mesenteric vein.Portal vein obstruction due to chronic liver disease,neoplasm, or post surgery is considered a separate entity and is not the same as extrahepatic portal vein obstruction
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Scholar S. Devaraj, D. Y. Xu, and I. Jialal, “C-reactive protein increases plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression and activity in human aortic endothelial cells:implications for the metabolic syndrome and atherothrombosis.,” Circulation,vol. 107, no.3, pp. 398–404, 2003. View at Google •
S.R.Lentz,M. Tsiang, and J. E.Sadler, “Regulation of thrombomodulin by tumor necrosis factor-α: comparison of transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms,” Blood, vol. 77, no. , pp. 542–550, 1991. View at Google Scholar •
K. L. Moore, C. T. Esmon, and N. L. Esmon,“Tumor necrosis factor leads to the internalization and de gradation of thrombomodulin from the surface of bovine aortic endothelium cells in culture,” Blood, vol.73, no. 1, pp.159–165, 1989. View at Google Scholar.
E. M. Conway and R. D. Rosenberg,“Tumor necrosis factor suppresses transcription of the thrombomodulin gene in endothelial cells,” Molecular and Cellular Biology, vol.8,no.12,pp.5588–5592, 1988. View at Google Scholar
R.Kerr,D.Stirling,andC.A.Ludlam,“Interleukin6 and haemostasis,”British Journal of Haematology, vol.115,no. 1, pp. 3–12, 2001.
B.K.Mahmoodi,M.K.Ten Kate, F. Waanders et al.,“High absolute risks and predictors of venous and arterial thromboembolic events in patients with nephrotic syndrome:results from a large retrospective cohort study,” Circulation,vol.117,no.2,pp.224–230, 2008. View at Publisher •
Valla DC,Condat , Lebrec D. Spectrum of portal veinthrombosis in the West.J Gastroenterol Hepatol.2002;17 (Suppl 3):S224–7.
Sarin SK, Sollano JD, Chawla YK, Amarapurkar D,Hamid ,Hashizume M, et al. Consensus on extra-hepatic portal vein obstruction. Liver Int. 2006;26:512–9.
JanssenHL, MeinardiJR ,Vleggaar FP,van UumSH, Haagsma EB,van Der Meer FJ, et al.Factor V Leiden mutation, prothrombin gene mutation,and deficiencies in coagulation inhibitors associated with Budd-Chiari syndrome and portal vein thrombosis: Results of a case-control study. Blood. 2000;96:2364–8.
Cohen J, Edelman RR, Chopra S. Portal vein thrombosis:A review.Am J Med.1992;92:173–82.
FiresteinG,Kelley.WKelley'stextbook of rheumatology Philadelphia,PA:Elsevier/Saunders; 2013.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr M.G.R. Medical University