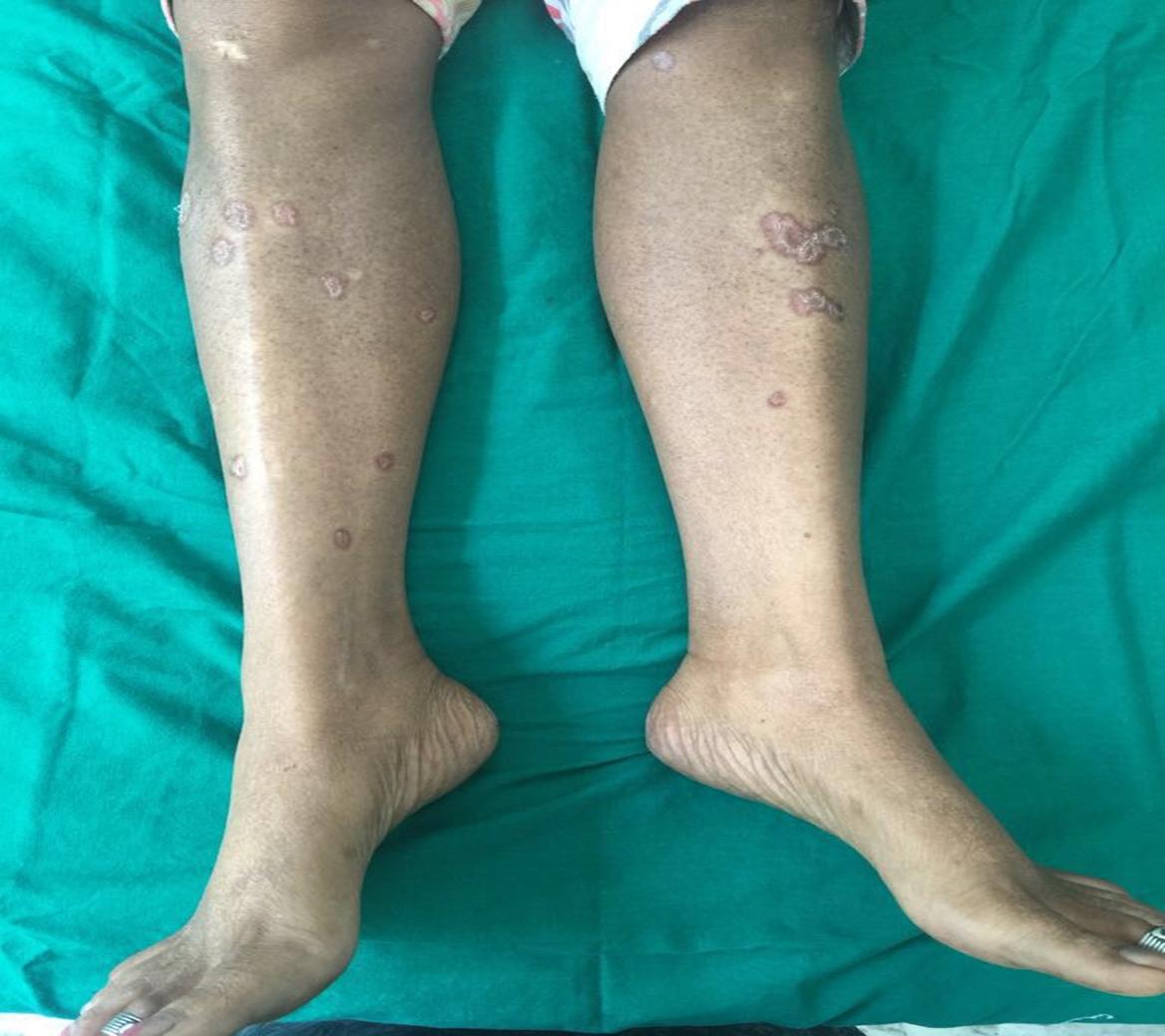
An interesting case of Sarcoidosis with cutaneous manifestations - A case report
Abstract
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Yanardag H, Pamuk O, Karayel T. Cutaneous involvement in sarcoidosis: analysis of the features in 170 patients. RespirMed. 2003;97:978–982.
Burgoyne J, Wood M.Psoriasiformsarcoidosis. Arch Der matol. 1972;106:896–898.
Reddy RR, Kumar BS, Harish MR. Cutaneous sarcoidosis-a great masquerader: a report of three interesting cases. Indian journal of dermatology. 2011 Sep;56(5):568
Marchell R, Judson M. Chronic cutaneous lesions of sarcoidosis. Clinics in Dermatol. 2007;25:295–302.
Farmer J, Winkelmann K. Psoriasis in association with sarcoidosis. Arch Dermatol. 1960;81:149–152.
Haimovic A, Sanchez M, Judson M, Prystowsky S. Sarcoidosis: a comprehensive review and update for the dermatologist. JAmAcadDermatol. 2012;66 (5):699.e1–719.e10.
Callejas-Rubio J, Ortego-Centeno N, Lopez-Perez L,Benticuaga M. Treatment of therapy-resistant sarcoidosiswithadalimumab. ClinRheumatol. 2006;25:596–597.
Lowes M, Bowcock A, Krueger J. Pathogenesis and therapy of psoriasis. Nature. 2007;445:866–873.
Victor F, Gottlieb A. TNF-alpha and apoptosis: implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of psoriasis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2002;1(3):264–275.
Mussi A, Bonifati C, Carducci M, et al. Serum TNF- alpha levels correlate with disease severity and are reduced by effective therapy in plaque-type psoriasis. J BiolRegHomeosAg. 1997;11(3):115–118.
Mak RKH, Hundhausen C, Nestle FO. Progress in understanding the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis.ActasDermosifiliogr. 2009;100(Suppl2): 2–13.
Baughman R, Lower E. Evidence-based therapy for cutaneous sarcoidosis. ClinDermatol. 2007;25: 334– 340.
Baughman R, Lower E. Infliximab for refractory sarcoidosis.SarcoidosisVasc Dif. 2001;18:70–74.
Doty J, Mazur J, Judson M. Treatment of sarcoidosis with infliximab. Chest. 2005;127:1064–1071.
Mallbris L, LjungbergA,Hedblad MA, et al. Progressive cutaneous sarcoidosis responding to anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy. J Am AcadDermatol. 2003;48:290–293.
Haley H, Cantrell W, Smith K. Infliximab therapy forsarcoidosis (lupus pernio). Br J Dermatol. 2004;150:146–149.
Loza M, Brodmerkel C, Du Bois RM, et al. Inflammatory profile and response to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in patients with chronic pulmonary sarcoidosis. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2011;18(6):931–939.
Aguiar M, Marcal N, Mendes AC, et al. Infliximab for treating sarcoidosis patients, Portuguese experience. Rev Port Pneumol. 2011;17(2):85–93.Keller copy_Layout 1 4/11/16 3:30 PM Page 57
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr M.G.R. Medical University