A Rare Case Report : Ataxia Telangiectasia
Abstract
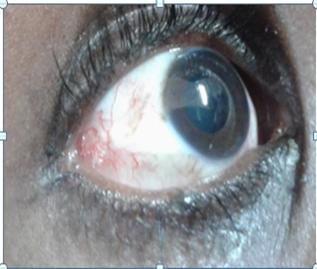
Ataxia Telangiectasia is a rare inherited as autosomal recessive disease with progressive degeneration of multisystem disorder. A-T is characterized by progressive cerebellar degeneration(1),oculo cutaneous telangiectasia, immunodeficiency,recurrent sinopulmonary infections, radiation sensitivity, premature aging, and predisposition to cancer development. Ataxia and Telangiectasias are the hallmarks of the disease. There is no gold standard diagnostic test and diagnosis relies on clinical evaluation and supportive laboratory tests .More than 99% of individuals with A-T have mutations in ATM gene mapped on 11q22-23, the only gene known to be associated with ataxia- telangiectasia.
We report a 17 years old girl who was presented in our hospital with respiratory failure with history of unsteady gait, frequent falls, repeated chest infections, and telangectasias of the eyes.
Keywords: Ataxia telangectasia, Immunodeficiency, neurodegenerative disease, alpha – fetoprotein (AFP), carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA).
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Smith, larry L.et al.Ataxia- telangectasia or Louis – Bar syndrome.J Am Acao Dermatol12:681696,1985.
Border E,Sedwick RP.Ataxia — telangectasia;a familial syndrome of progressive cerebellar ataxia, oculo cutaneous telangectasia and Frequent pulmonary infection,Pediatrics,1958;21:526-54 Abraham RT.cell cycle checkpoint signalling through the ATM and ATR kinases.Genes Dev.2001;15:2177-96.
Lavin MF, Shiloh Y. The genetic defectin ataxia telangiectasia. Ann RevImmunol. 1997; 15: 177-202.
ShilohY. ATMandrelatedproteinkinases: safeguarding genome integrity.Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2003; 3: 155-68.
Shiloh Y, Kastan MB. ATM. Genome stability, neuronal development, and cancer cross paths. Adv Cancer Res.2001; 83: 209-54
Kastan MB, Lim DS. The many substrates and functions of ATM. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000; 1: 179-86.
Perlman S, Becker-Catania S, Gatti RA. Ataxia-telangiectasia: diagnosis and treatment. Semin PediatrNeurol2003;10:173- 82.
CabanaMD;Crawford,To,Winkelstein,JA,Christensen, JR, Lederman, HM(21998 Jul),”Consequences of the delayeddiagnosis of ataxia-telangiectasia.”Pediatrics 102 (1pt1):98-100.
Cohen MMJR.Levy Hp. Chromosom instability syndrome. Adv Hum Genet1989;18;43-149.
Nowak-Wegrzyn A, et al. Immunodeficiency and infections inataxia-telangiectasia. J Pediatr. 2004;144 (4): 505–11.
Driessen GJ, et al. Antibody deficiency in patients with ataxia telangiectasia is caused by disturbed B- and T-cellhomeostasis and reduced immune repertoire diversity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131(5):1367–75.
Lefton-Greif MA, et al. Oropharyngeal dysphagia and aspiration in patients with ataxia-telangiectasia. J Pediatr. 2000;136 (2):225–31 13.
Gatti RA, Vinters HV. Cerebellar pathology in ataxia-telangiectasia: the significance of basket cells. Kroc Found Ser. 1985;19:225–32
Stray-Pedersen A, Borresen-Dale AL, Paus E, Lindman CR, Burgers T,Abrahamsen TG. Alpha fetoprotein is increasing with age in ataxia – telangiectasia. European journal of paediatric neurology. 2007 Nov 30;11(6):375-80.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr M.G.R. Medical University