Effect of Metformin and Hydroxy Chloroquine Combination on Blood Glucose in Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats
Abstract
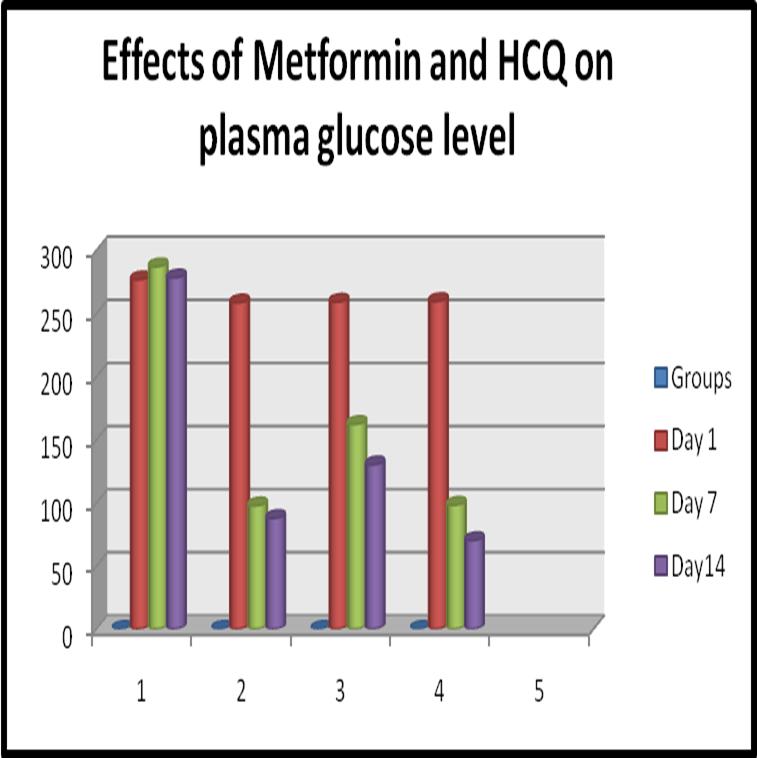
Aim and Objective : To investigate the effect of Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) alone and in combination with Metformin on glycemic control on Streptozotocin induced diabetic rats.
Methodolody : 24 inbred adult male albino rats weighing 150 to 200 grams from central animal house, Madurai were utilized for the study. They will be divided into 4 groups of 6 animals each. Animals were allowed feed on standard diet (pellet feed) , tap water ad libitum. Streptozotocin was used to induce diabetes in the albino rats. Streptozotocin was given at the dose of 60mg/kg intraperitoneally as a single dose after overnight fasting. Group 1 (normal control) consisted of normal rats that neither received any drug. Rats in Group 2 were diabetic and treated with Metformin 200mg/kg orally. Rats in Group 3 were diabetic and treated with Hydroxychloroquine 200 mg/kg orally . Animals in Group 4 were diabetic and treated with combination of Metformin and Hydroxychloroquine(200 mg/kg orally . The drugs were given once daily for 14 days.
Results : In Streptozotocin induced diabetic rats, Hydroxychloroquine with Metformin combination therapy reduced blood glucose level significantly (P< 0.001) then used alone.
Conclusion : Outcomes of this investigation indicate that combination of Metformin with HCQ improves glycemic control and provides additional metabolic benefits, not achieved with either HCQ or metformin used alone. The combination of Metformin and Hydroxychloroquine exhibited the most significant reduction in glucose level by its peripheral action i.e, extrapancreatic action.
Key Words : Metformin, Hydroxychloroquine, Streptozotocin, blood glucose, glucometer
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Zannah, S., et al. (2014) Antidiabetic Drugs in Combination with Hydroxychloroquine Improve Glycemic Control in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats. Pharmacology & Pharmacy, 5, 725-735. http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/pp.2014.57082
King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH. Global burden of diadetes, 1995-2025:prevalence, numerical estimates and projections.Diabetes care 1998;21:1414-31 [PUBMED]
Defronzo, R.A. and Goodman, A.M. (1995) Efficacy of Metformin in Patient with Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. The New England Journal of Medicine, 333, 541-549. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199508313330902
Bertram G. Katzung, Anthony J. Trevor. Endocrine drugs: Pancreatic hormones and Antidiabetic drugs. In. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology,13th edition. New Delhi: McGraw-Hill Education (India) Private Limited, 2015: page 736.
Morand EF, Mc Cloud PI,Littlejohn GO.Continuation of long term treatment with hydroxychloroquine in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis 1992;51:1318-21.[PUBMED]
Hertzel Gerstein C, Kevin Thorpe E,Wayne Taylor D,Brian Haynes R. The effectiveness of hydroxychloroquine in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who are refra tory to sulfonylurea- a randomized trial.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2002;55:209-19 [PubMed]
Emami J,Gerstein HC,Pasutto FM,Jamali F.Insulin sparing effect of HCQ in diabetic rats in concentration dependent.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1999;77:118-23.
D.Ü. Cansu and C. Korkmaz. Hypoglycaemia induced by hydroxychloroquine in a non-diabetic patient treated for RA. Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, December 18,2007. E-mail: ckorkmaz@ogu.edu.tr
Emami J,Pasutto FM,Mercer JR,Jamali F.Inhibition of insulin metabolism by hydroxychloroquine and its enantiomers in cytosolic fraction of liver homogenates from healthy and diabetic ratr.Life Sciences. 1999;64: 325-35.
Grove, J.K., Vats, V. and Rath,S.S. (2000) Antihyperglycenic Effect of Eugenia Jambolana and Tinosporacardifolia In Expiremntal Diabetes and Their Effects on Key Metabolic Enzymes Involved In Carbohydrate Metabolism. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 73, 461-470.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr M.G.R. Medical University