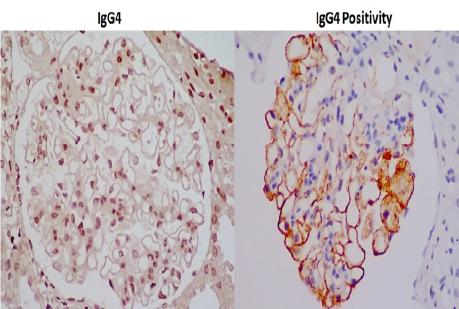
IgG4 Immunostaining in Membranous Nephropathy
Abstract
Background: Membranous nephropathy (MN) is the
most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in adults.
Detection of phospholipase A2 receptor (APLA2R) antigen and
its dominant IgG4 autoantibody in glomerular deposit of
patient with MN was useful for the differentiation between
primary MN and secondary MN. Aim: To study the IgG4
staining pattern in renal biopsy in patients with membranous
nephropathy. Materials and methods: Retrospective study of
17 cases of MN diagnosed on renal biopsy were analysed.
The formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissues were stained
with routine hematoxylin and eosin stains along with periodic
acid Schiff and silver methenamine stains to highlight
basement membrane. Immunostaining with IgG4 antibodies
were done. Tissue APLA2 R was not done. IgG4
antibodies can be detected in the glomerular immune
complexes and they colocalize with APLA2 R. In secondary
forms of membranous nephropathy, such IgG4 antibodies are
absent or less prevalent. Results: A total of 17 biopsy proven
membranous nephropathy were analysed. About 53% were
males. The most common presentation was nephrotic
syndrome (58%), followed by renal failure (17.6%) and
sub-nephrotic proteinuria (17.6%). Serum PLA2R antibody
was positive in 4 (23.5%) of 17 patients with primary MN but in
none of the patients with secondary MN. IgG4 immunostaining
in glomerular capillaries was done in all biopsy specimens.
Among the APLA2R antibod y positive patients, 3 (75%) had
positivity for igG4 immunostaining in biopsy. In 5 patients with
secondary MN only 1 patient (20%) showed positivity for
igG4 immunostaining. Conclusion: There is significant
concordance between serum APLA2 R antibody positivity and
IgG4 staining (75%). IgG4 immunostaining in kidney biopsy
can be considered as a marker of idiopathic membranous
nephropathy.
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Beck LH Jr, Bonegio RG, Lambeau G, Beck DM, Powell
DW, Cummins TD, et al. M-type phospholipase A2 receptor
as target antigen in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N
Engl J Med. 2009; 361: 11–21. doi: 10.1056/
NEJMoa0810457 [PMC free article] (PubMed).
Beck LH Jr, Salant DJ. Membranous nephropathy: recent
travels and new roads ahead. Kidney Int. 2010; 77: 765–770.
doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.34 [PubMed].
Allison SJ. Glomerular disease: Thrombospondin type-1
domain-containing 7A-a new player in membranous
nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015; 11: 63 doi: 10.1038/
nrneph.2014.227 (PubMed).
Huang CC, Lehman A, Albawardi A, Satoskar A, Brodsky
S, Nadasdy G, et al. IgG subclass staining in renal biopsies
with membranous glomerulonephritis indicates subclass
switch during disease progression. Mod Pathol. 2013; 26:799
–805. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2012.237 [PubMed].
Hofstra JM, Debiec H, Short CD, Pellé T, Kleta R,
Mathieson PW, et al. Antiphospholipase A2 receptor antibody
titer and subclass in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 2012; 23: 1735–1743. (PMC free article).
Nirula A, Glaser SM, Kalled SL, Taylor FR. What is IgG4?
A review of the biology of a unique immunoglobulin subtype.
Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011; 23: 119–124. doi: 10.1097/
BOR.0b013e3283412fd4 [PubMed].
Filippone EJ. Idiopathic membranous nephropathy and
IgG4: an interesting relationship. Clin Nephrol. 2014; 82:
-15. doi: 10.5414/CN107768 [PMC free article] [PubMed).
Huang CC, Lehman A, Albawardi A, et al. IgG subclass
staining in renal biopsies with membranous glomerulonephritis
indicates subclass switch during disease progression.
Mod Pathol. 2013; 26:799–805. doi: 10.1038/
modpathol.2012.237 [PubMed].
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr M.G.R. Medical University