RASMUSSENS ENCEPHALITIS - A CASE REPORT
Abstract
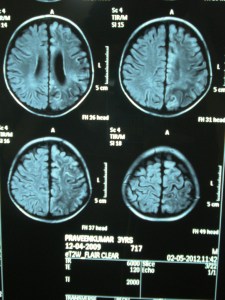
CASE HISTORY A 3 year old boy presented with status epilepticus, aphasia and right hemiparesis. On evaluation he was found to have atropy of left cerebral cortex on MRI and Unilateral slowing and epileptiform activity on left side in EEG. He was diagnosed to have RE as per EUROPEAN CONSENSUS STATEMENT. INTRODUCTION RE is a chronic progressive, inflammatory disease of the brain affecting one hemisphere. The characteristic feature inclue Epilepsia Partialis Continua, hemiparesis, congnitive disturbances and speech disturbances. ETIOLOGY It is of unknown etiology. The postulated hypothesis include direct viral insult, primary autoimmune injury and immune response secondary to viral infection. DIAGNOSIS The diagnostic criteria as proposed by European consensus statement 2005 has primary and secondary criteria. The primary criteria includes Clinical (partial seizures and unilateral neurological deficits), MRI(unilateral focal cortical atropy and T2FLAIR hyperintense signal or atropy of head of caudate nucleus) and EEG (Unilateral slowing with or without epileptiform activity, unilateral ictal onset).The Secondary criteria includes Clinical (EPC or progressive unilateral neurological deficit), MRI(progressive unilateral focal cortical atrophy) and Histopathology (T-lymphocyte dominated encephalitis with activated microglial cells and reactive astrogliosis.TREATMENT The various treatment modalities include anticonvulsants, physiotherapy, immunotherapy, plasmapheresis, Monoclonal antibodies and surgical procedures like functional hemispherectomy.
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Rasmussen`s encephalitis, created 05/2003 Last updated 07/2005.by Dr.Ian Hart,senior lecturer in neurology, Neuroimmuology group,university department of neurological science.Lower lane,LIverpool.
Rasmussens encephalitis: An overview- Mayowa owolabi,university of Ibadan,Nigeria.
Rassmussens Encephalitis: an update by Laurent sheybani,Karl schaller,Margitta seeck 2011.
Chinchilla D,Dulac O, Robain O, Plouin P, Ponsot G, Pinel JF, Graber D, -Reappraisal of Rasmussens`s syndrome with special emphasis on treatment with high doses of steroids.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiarty 1994;57:1325-33.
Hart YM, Cortez M, Andermann F, Hwang P, Fish Dr, Dulac O, et al. Medical treatment of Rasmussen`s syndrome ( chronic encephalitis and epilepsy); effect of high-dose steroids or immunoglobulins in 19 patients.Neurology 1994;44:1030-6.
Leach JP, Chadwick DW, Miles JB, Hart IK. Improvement in adult-onset Rasmussen’s encephalitis with long-term immunomodulatory therapy. Neurology. 1999;52(4):738–42.
Leach JP, Chadwick DW, Miles JB, Hart IK. Improvement in adult-onset Rasmussen’s encephalitis with long-term immunomodulatory therapy.Neurology. 1999;52(4):738–42.
Wise MS, Rutledge SL, Kuzniecky RI. Rasmussen syndrome and long-term response to gamma globulin. Pediatr Neurol. 1996;14:149–52.
Granata T, Fusco L, Gobbi G, Freri E, Ragona F, Broggi G, et al. Experience with immunomodulatory treatments in Rasmussen’s encephalitis.Neurology. 2003;61(12): 1807–10.
Bien CG, Gleissner U, Sassen R, Widman G, Urbach H, Elger CE. An open study of tacrolimus therapy in Rasmussen encephalitis. Neurology. 2004;62(11):2106–9.
Thilo B, Stingele R, Knudsen K, Boor R, Bien CG, Deuschl G, Lang N.A case of Rasmussen encephalitis treated with rituximab. Nat Rev Neurol.2009;5(8):458–12)Pulsifer MB, Brandt J, Salorio CF, Vining EP, Carson BS, Freeman JM.The cognitive outcome of hemispherectomy in 71 children. Epilepsia. 2004;45:243.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
An initiative of The Tamil Nadu Dr M.G.R. Medical University